1. What is Hibernate Framework?
Object-relational mapping or ORM is the programming technique to map application domain model objects to the relational database tables. Hibernate is Java-based ORM tool that provides a framework for mapping application domain objects to the relational database tables and vice versa.
Hibernate provides a reference implementation of Java Persistence API, that makes it a great choice as ORM tool with benefits of loose coupling. We can use the Hibernate persistence API for CRUD operations. Hibernate framework provide option to map plain old java objects to traditional database tables with the use of JPA annotations as well as XML based configuration.
Similarly, hibernate configurations are flexible and can be done from XML configuration file as well as programmatically.
2. What are the important benefits of using Hibernate Framework?
Some of the important benefits of using hibernate framework are:
- Hibernate eliminates all the boiler-plate code that comes with JDBC and takes care of managing resources, so we can focus on business logic.
- Hibernate framework provides support for XML as well as JPA annotations, that makes our code implementation independent.
- Hibernate provides a powerful query language (HQL) that is similar to SQL. However, HQL is fully object-oriented and understands concepts like inheritance, polymorphism, and association.
- Hibernate is an open source project from Red Hat Community and used worldwide. This makes it a better choice than others because learning curve is small and there are tons of online documentation and help is easily available in forums.
- Hibernate is easy to integrate with other Java EE frameworks, it’s so popular that Spring Framework provides built-in support for integrating hibernate with Spring applications.
- Hibernate supports lazy initialization using proxy objects and perform actual database queries only when it’s required.
- Hibernate cache helps us in getting better performance.
- For database vendor specific feature, hibernate is suitable because we can also execute native sql queries.
Overall hibernate is the best choice in current market for ORM tool, it contains all the features that you will ever need in an ORM tool.
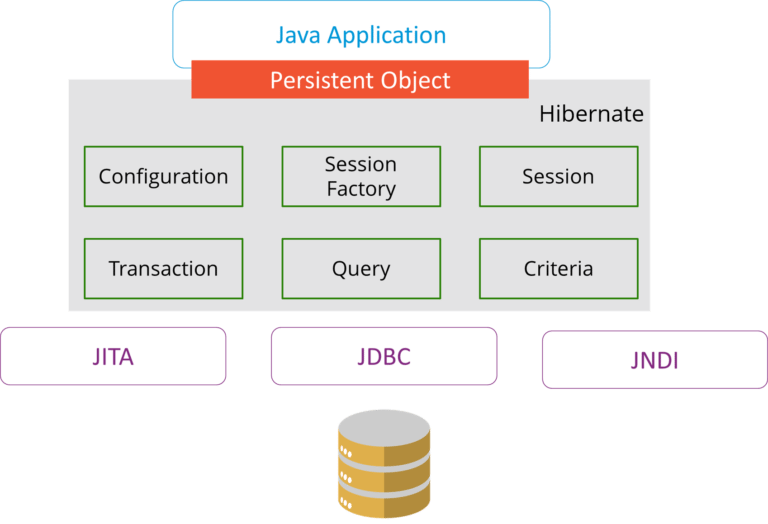
3. Explain Hibernate architecture.
4. What are the differences between get and load methods?
The differences between get() and load() methods are given below.
| No. | get() | load() |
| 1) | Returns null if object is not found. | Throws ObjectNotFoundException if an object is not found. |
| 2) | get() method always hit the database. | load() method doesn’t hit the database. |
| 3) | It returns a real object, not a proxy. | It returns a proxy object. |
| 4) | It should be used if you are not sure about the existence of instance. | It should be used if you are sure that the instance exists. |
5. What are the advantages of Hibernate over JDBC?
Some of the important advantages of Hibernate framework over JDBC are:
- Hibernate removes a lot of boiler-plate code that comes with JDBC API, the code looks cleaner and readable.
- Hibernate supports inheritance, associations, and collections. These features are not present with JDBC API.
- Hibernate implicitly provides transaction management, in fact, most of the queries can’t be executed outside transaction. In JDBC API, we need to write code for transaction management using commit and rollback.
- JDBC API throws SQLException that is a checked exception, so we need to write a lot of try-catch block code. Most of the times it’s redundant in every JDBC call and used for transaction management. Hibernate wraps JDBC exceptions and throw JDBCException or HibernateException un-checked exception, so we don’t need to write code to handle it. Hibernate built-in transaction management removes the usage of try-catch blocks.
- Hibernate Query Language (HQL) is more object-oriented and close to Java programming language. For JDBC, we need to write native SQL queries.
- Hibernate supports caching that is better for performance, JDBC queries are not cached hence performance is low.
- Hibernate provides option through which we can create database tables too, for JDBC tables must exist in the database.
- Hibernate configuration helps us in using JDBC like connection as well as JNDI DataSource for the connection pool. This is a very important feature in enterprise application and completely missing in JDBC API.
- Hibernate supports JPA annotations, so the code is independent of the implementation and easily replaceable with other ORM tools. JDBC code is very tightly coupled with the application.